Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Optics and Optical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 International Quantum Academy, Shenzhen 518048, China
3 Shenzhen Institute for Quantum Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
4 Hefei National Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230088, China
5 e-mail: atwang@ustc.edu.cn
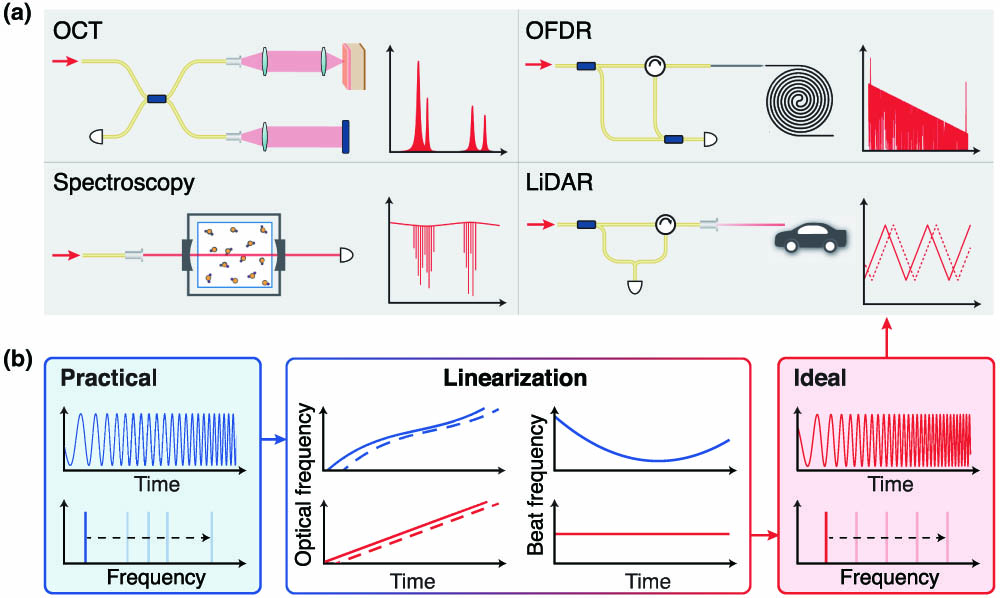
Tunable lasers, with the ability to continuously vary their emission wavelengths, have found widespread applications across various fields such as biomedical imaging, coherent ranging, optical communications, and spectroscopy. In these applications, a wide chirp range is advantageous for large spectral coverage and high frequency resolution. Besides, the frequency accuracy and precision also depend critically on the chirp linearity of the laser. While extensive efforts have been made on the development of many kinds of frequency-agile, widely tunable, narrow-linewidth lasers, wideband yet precise methods to characterize and linearize laser chirp dynamics are also demanded. Here we present an approach to characterize laser chirp dynamics using an optical frequency comb. The instantaneous laser frequency is tracked over terahertz bandwidth at 1 MHz intervals. Using this approach we calibrate the chirp performance of 12 tunable lasers from Toptica, Santec, New Focus, EXFO, and NKT that are commonly used in fiber optics and integrated photonics. In addition, with acquired knowledge of laser chirp dynamics, we demonstrate a simple frequency-linearization scheme that enables coherent ranging without any optical or electronic linearization unit. Our approach not only presents novel wideband, high-resolution laser spectroscopy, but is also critical for sensing applications with ever-increasing requirements on performance.
Photonics Research
2024, 12(4): 663

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Integrated Circuit Science and Engineering, Hefei Innovation Research Institute, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2 Anhui High Reliability Chips Engineering Laboratory, Hefei 230013, China
3 School of Energy and Power Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
4 Department of Optics and Optical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
5 Institut Jean Lamour, UMR CNRS 7198, Universite de Lorraine, Nancy 54011, France
6 e-mail: yongxu@buaa.edu.cn
In spintronic applications, there is a constant demand for lower power consumption, high densities, and fast writing speed of data storage. All-optical switching (AOS) is a technique that uses laser pulses to switch the magnetic state of a recording medium without any external devices, offering unsurpassed recording rates and a simple structure. Despite extensive research on the mechanism of AOS, low energy consumption and fast magnetization reversing remain challenging engineering questions. In this paper, we propose a newly designed cavity-enhanced AOS in GdCo alloy, which promotes optical absorption by twofold, leading to a 50% reduction in energy consumption. Additionally, the time-resolved measurement shows that the time of reversing magnetization reduces at the same time. This new approach makes AOS an ideal solution for energy-effective and fast magnetic recording, paving the way for future developments in high-speed, low-power-consumption data recording devices.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(11): 1870
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Optics and Optical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 School of Optical-Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
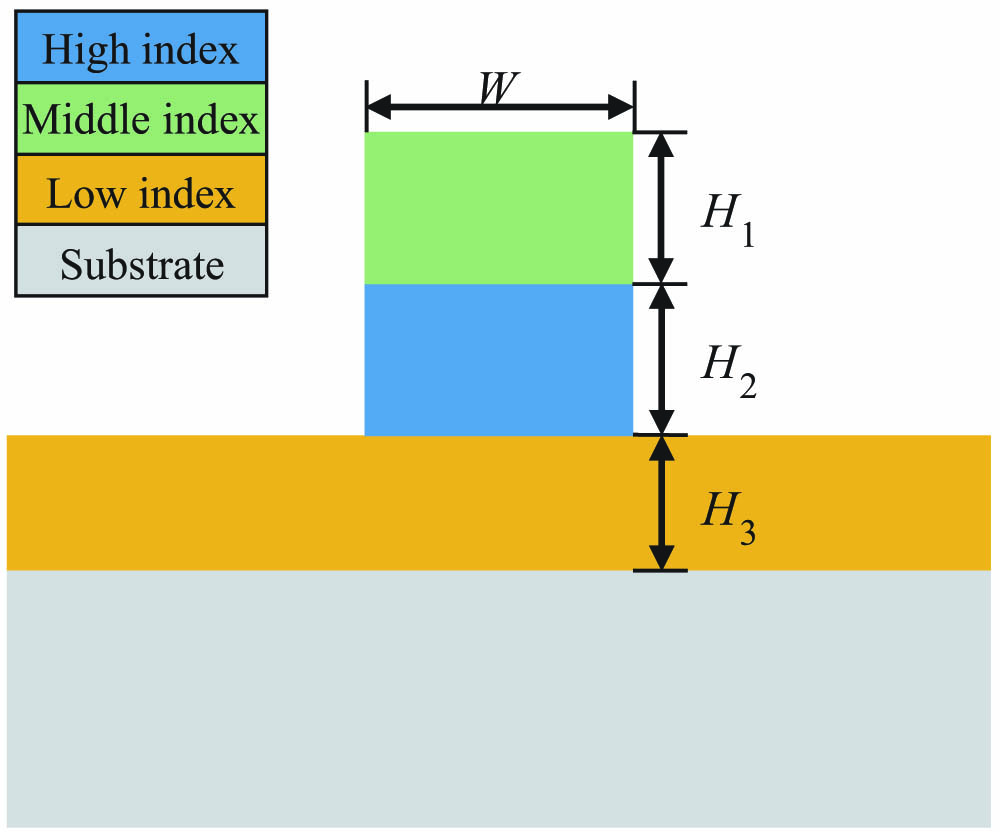
We propose a new type of dispersion-flattened waveguide without a slot-assisted structure that can obtain an ultra-flat group velocity dispersion profile with five or six zero-dispersion wavelengths in the mid-infrared region. The dispersion profile becomes less sensitive to the waveguide dimensions due to the absence of the slot-assisted structure, making waveguide fabrication more friendly. The dispersion profile varies between and ps/(nm · km) over a 2665 nm bandwidth from 2885 nm to 5550 nm with a flatness of nm2 · km/ps. Two different combinations of materials are demonstrated for dispersion flattening of the proposed waveguide structures. We also provide design guidance for the proposed waveguide structures with other combinations of materials.
integrated optical devices waveguides dispersion Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(10): 101302

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Integrated Circuit Science and Engineering, Hefei Innovation Research Insititute, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2 Anhui High Reliability Chips Engineering Laboratory, Hefei 230013, China
3 School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xiangtan University, Xiangtan 411105, China
4 Department of Optics and Optical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
5 School of Optical-Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
Spectral fingerprint and terahertz (THz) field-induced carrier dynamics demands the exploration of broadband and intense THz signal sources. Spintronic THz emitters (STEs), with high stability, a low cost, and an ultrabroad bandwidth, have been a hot topic in the field of THz sources. One of the main barriers to their practical application is lack of an STE with strong radiation intensity. Here, through the combination of optical physics and ultrafast photonics, the Tamm plasmon coupling (TPC) facilitating THz radiation is realized between spin THz thin films and photonic crystal structures. Simulation results show that the spectral absorptance can be increased from 36.8% to 94.3% for spin THz thin films with TPC. This coupling with narrowband resonance not only improves the optical-to-spin conversion efficiency, but also guarantees THz transmission with a negligible loss () for the photonic crystal structure. According to the simulation, we prepared this structure successfully and experimentally realized a 264% THz radiation enhancement. Furthermore, the spin THz thin films with TPC exhibited invariant absorptivity under different polarization modes of the pump beam and weakening confinement on an obliquely incident pump laser. This approach is easy to implement and offers possibilities to overcome compatibility issues between the optical structure design and low energy consumption for ultrafast THz opto-spintronics and other similar devices.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(6): 1057

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Hefei Innovation Research Institute, School of Microelectronics, Beihang University, Hefei 230013, China
2 Fert Beijing Institute, BDBC, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
3 Advanced Photonics Center, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
4 Department of Optics and Optical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
All-optical magnetization switching with features of low-power consumption and high writing speed is a promising road map to satisfy the demand for volume data storage. To promote denser and faster magnetic recording technologies, herein, all-optical helicity-dependent switching (AO-HDS) in multi-layer magnetic recording is proposed based on the chromatic aberration of an optical lens (Thorlabs’s N-BK7 plano-convex uncoated lens). The power of the incident beams and the thickness of the multi-layer magnetic recording film are designed carefully. Besides, the uniformity of this multi-layer magnetic recording is optimized. At last, a prototype system of information multiplexing based on this multi-layer magnetic recording technology is constructed as well. Flexible and controllable magnetization reversals in different layers are also demonstrated by tuning the wavelength and helicity of working beams. We believe that such a prototype system can pave the way for increasing the storage density in an effective and low-cost mode.
all-optical magnetization switching multi-level magnetic recording focal shift chromatic aberration Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(10): 102501

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Optics and Optical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 Hefei General Machinery Research Institute, Hefei 230031, China
In this work, an all-fiber-based mode converter for generating orbital angular momentum (OAM) beams is proposed and numerically investigated. Its structure is constructed by cascading a mode selective coupler (MSC) and an inner elliptical cladding fiber (IECF). OAM modes refer to a combination of two orthogonal LPlm modes with a phase difference of ±π/2. By adjusting the parameters and controlling the splicing angle of MSC and IECF appropriately, higher-order OAM modes with topological charges of l = ±1, ±2, ±3 can be obtained with the injection of the fundamental mode LP01, resulting in a mode-conversion efficiency of almost 100%. This achievement may pave the way towards the realization of a compact, all-fiber, and high-efficiency device for increasing the transmission capacity and spectral efficiency in optical communication systems with OAM mode multiplexing.
optical vortices fiber optics singular optics mode-division multiplexing Opto-Electronic Advances
2018, 1(7): 180003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Optics and Optical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
In this Letter, an effective method using a mode selective coupler (MSC), which is composed of a three-core fiber is presented to generate optical vortices (OVs). The conversions of OVs with different topological charges, 0→±1 and 0→±3, are simulated in detail. We also prove that a higher-order topological charge can be obtained simply by changing the parameters of the fiber to increase the number of modes in the fiber. The polarization of OVs can be controlled as well.
060.2310 Fiber optics 060.5060 Phase modulation 230.2285 Fiber devices and optical amplifiers 050.4865 Optical vortices Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(3): 030008
中国科学技术大学光学与光学工程系, 安徽 合肥 230026
为了消除多级像和零级光的干扰,提出了一种单透镜结构的系统,获得了单一无扰的再现像。 使用Gerchberg-Saxton(GS)算法获得菲涅尔全息图,预先叠加倾斜平面波相位至菲涅尔全息图上,使再 现像移至中央位置。用成像透镜将空间光调制器(SLM)后方的虚像成像至前方,同时在成像透镜后方放置 空间滤波器,滤去多级像和零级光。调整透镜与SLM的位置可方便调整再现像的大小和位置, 缩短了光学系统的长度。利用虚像的方法为基于液晶SLM的计算全息显示提供了新的思路。
全息 空间光调制器 GS算法 纯相位全息图 holography spatial light modulator Gerchberg-Saxton algorithm phase-only hologram

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Optics and Optical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 Electro-Optics Program, University of Dayton, Dayton, Ohio 45469, USA
We demonstrate an all fiber passively mode-locked laser emitting a radially polarized beam by using a few-mode fiber Bragg grating to achieve mode selection and spectrum filtering. An offset splicing of single-mode fiber with four-mode fiber is utilized as a mode coupler in the laser cavity. Carbon nanotubes are introduced into the laser cavity as the saturable absorber to achieve self-start mode locking. The laser operates at 1547.5 nm with a narrow spectrum width of 0.3 nm at 30 dB. The emitted mode-locked pulses have a duration of 22.73 ps and repetition of 10.61 MHz. A radially polarized beam has been obtained with high mode purity by adjusting the polarization in the laser cavity.
Fibers Fibers erbium erbium Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Fiber Bragg gratings Fiber Bragg gratings Mode-locked lasers Mode-locked lasers Nanomaterials Nanomaterials Photonics Research
2016, 4(6): 06000327
1 中国科学技术大学光学与光学工程系, 安徽 合肥 230026
2 重庆卓美华视光电有限公司, 重庆 401520
人眼是三维显示的第一接受器官,在深度视觉、空间/时间分辨、颜色/亮度响应等过程有其独特作用。针对三维显示中的立体图像质量、观看舒适度和临场感特性,对自由立体显示器中立体视疲劳、表面形变、大视场角显示质量和色带效应进行研究,从柱透镜的脉冲响应函数出发进行分析,并提出解决方法,在此基础上将多视点自由立体显示用于澄江古生物群科普宣传。同时讨论了集成成像中单元图像处理、立体深度和显示分辨率的问题,以及全息显示技术中的人眼视觉特性。
视觉光学 三维显示 自由立体显示器 人眼视觉特性 集成成像 全息显示





